
Reducing Cost of Maintenance Dredging of a Sea Port
with
Alternate Basin Upkeep Techniques (ABUTs)
Successful implementation of Integrated Basin Upkeep System has to potential to reduce the Maintenance Dredging Cost of a Port substantially.
iBUS employs Alternate Basin Upkeep Techniques (ABUTs) which are innovative methods using advanced technologies to reduce or completely remove the need of recurrent dredging by conventional methods. A unique and port specific Alternate Basin Upkeep Plan (ABUP) is developed after studying the sediment characteristics, sediment transport process, local topography and characteristics features of the port and nearby water bodies.
Up to 80% Reduction in Maintenance Dredging Cost
Our Services
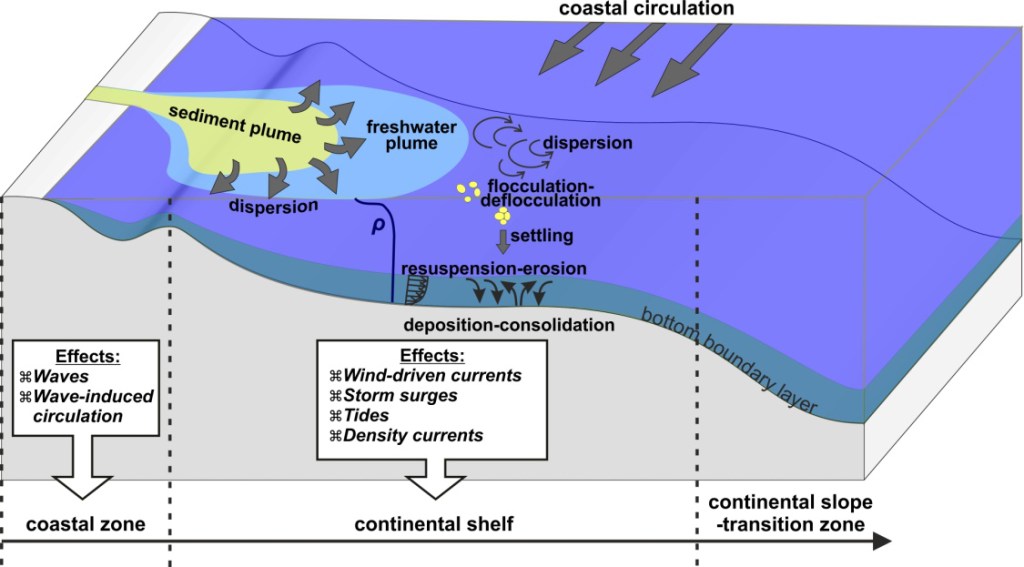
The objective is to identify the sources of sedimentation and their contribution to overall harbor sedimentation. We ascertain the sediment transport mechanism to understand the preventive measures that can be successfully taken.
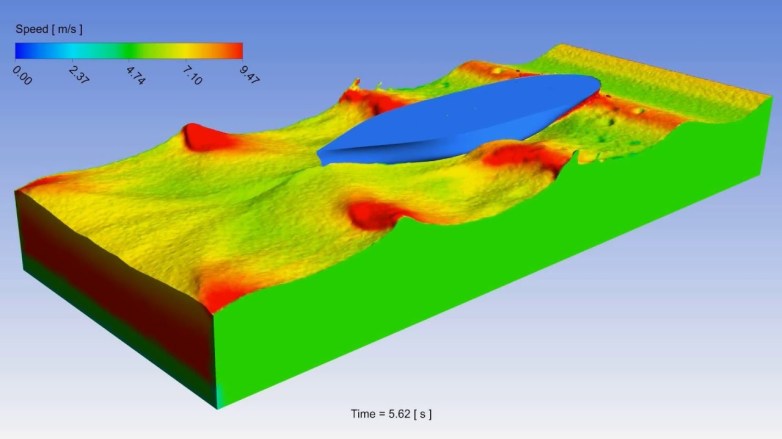
Computational Fluid Dynamics service is a reality today in marine and port operations. It has many advantages of understanding complex dynamics of water flow in harbor areas. It helps in avoiding difficult scenarios and waste of resources. It has been a main plank in planning and implementing cost effective systems in ports today.
We specialize in developing an integrated Basin Upkeep System (iBUS) with an objective of reduction or if possible compete removal of sediments into the harbor area by applying innovative and cost-effective systems. The systems are new and use alternative methods to conventional dredging.
We not only develop iBUS but also help our clients in implementing the iBUS up to the extent as required. We involve in the project management, cost analysis. We develop the most cost effective ways suitable to the project as per the customer requirement.
Additional Benefits of Our Innovative Solutions
Besides achieving the prime objective of cost reduction in recurrent and heavy annual maintenance dredging, We are proud to provide our clients with additional benefits inherent with our systems. Those advantages are:
+ Ports run at full capacity at all times without disturbance
+ Down time in port operation removed
+ Water quality improved and pollution reduced substantially
+ Reduction of carbon footprint with minimal fuel consumption
Maintenance dredging costs are heavy, recurrent, and raises profitability and sustainability of many ports facing severe sedimentation. We have developed alternate techniques that remove the need for conventional dredging. Adopting alternate techniques reduces annual costs substantially. Alongside the cost reduction, BUTs cut down the fuel consumption by the dredging activities drastically. Hence reducing carbon footprint and consequent pollution.
The global dredging market is estimated at USD 15.7 Billion in 2022 and is forecast to reach USD 21.4 Billion by 2032, growing with a CAGR of 3.3% from 2022 to 2032. The revenue generation of dredging is likely to accelerate at a steady CAGR of 3.3% to top USD 21.4 Billion by 2032. Further the demand for energy infrastructure in application is likely to increase at a CAGR of 4.5% over the forecast period of 2022 to 2032. As per Industry estimates, the Indian annual dredging market, was estimated as around 147 – 157 Million cubic meter (mcm) with maintenance dredging constituting around 70% of Indian dredging market.
With a futuristic outlook we are sure we will be able to reduce this huge cost to the ports while contributing towards the Global Green Agenda by cutting emissions from these dredging activities. We will strive towards making the Maritime Industry zero carbon emitting Industry. We are continuously working to innovate new methods, bring in new procedures, new working styles suitable to the future challenges.
How We Develop a Port-specific iBUS ?
Step-1: Review Existing Dredging Activities
Study, critically analyse and understand the existing recurrent activities of maintenance dredging . It includes the studying the dump area, types of dredgers used, quantity of dredging, cost per unit, cost calculation etc. Our study reveals the loopholes in the system and methods to plug in those. It aims to bring about utmost efficiency in the existing system.
Step-2: Hydrodynamics Study
We carry out hydrodynamic study of the harbor basin and adjacent water bodies. The study includes analyzing the sediment characteristics, water quality, predominant current, wind, wave pattern, cyclonic conditions and their effects, predominant alongshore drift, fluvial sediments etc. By this we understand the historical time frame and spatial distribution of sedimentation. The aim of the study is to identify the sources of sediments and understand the characteristics of sediment transport mechanism acting on the harbor.
Step-2: Devise a Tentative Basin Upkeep Plan (BUP) with Detailed Measures
Understanding the spatial and historical distribution of local hydrodynamics and sources of sedimentation, it will be clear on which methods are best suitable to be applied at different locations of the harbor area to reduce substantial sedimentation or if possible completely eliminate the sediments from entering the harbor. For this we may use Sediment Barrier-Trap System (SBTS) or Fixed De-Silting System (FDSS) or Long-shore Sediment Management System (LSMS) or a combination of these systems. These systems use no use of conventional dredger to do the job rather innovative use of technologies are being done. These systems use little or no use of fuel for running, instead we use electricity from shore.
Step-4: Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) Study of all the Components of BUP
Carry out a Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) study of the specific systems to be used in devising the BUP. From CFD analysis it will be well clear on the percentage of efficiency that can be achieved. If need be there will be some modifications in the BUP to develop the final iBUS.
Step-5: Develop Integrated Basin Management Plan
As per the result of the analysis, develop a best suitable, effective and port specific Integrated Basin Upkeep Plan (iBUS). Sediment Barrier-Trap System (SBTS) or Fixed De-Silting System (FDSS) or Long-shore Sediment Management System (LSMS) or a combination of these systems. It employs in-situ sediment barriers of specialized geo-fabrics, deflection barriers, bubble curtains, coagulants, turbidity barriers, sediment tanks, sediment re-suspender and periodic flushing of fresh sediments, and fixed de-siltation systems depending upon the need of the site. Our specialist team knows the best.

Contact Us
To explore our services, contact us

Cost effective, reduced time delays and improving on carbon footprint of industries.
We promote Environmental Conscious Business.
Use Our Innovative Methods and Solve the Economic Woos of Your Organisation
Green Operations and Green Procedures with reduced cost and improved safety standards. We feel concerned and We care for the future.
